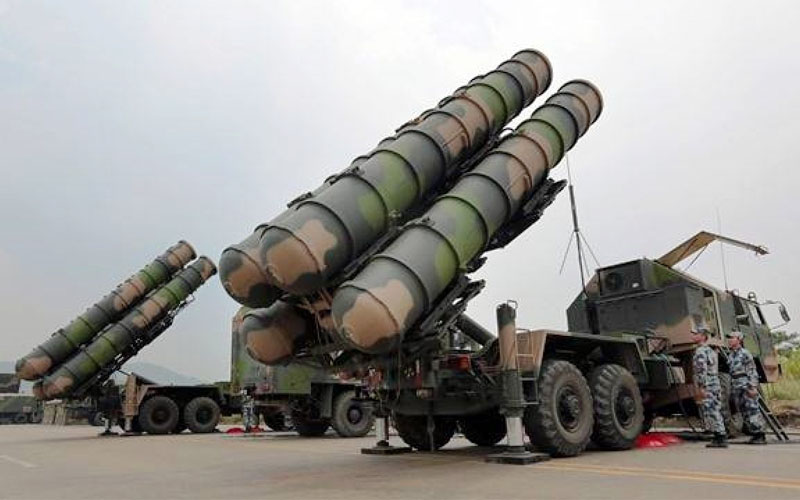
The draft budget for 2026 has revealed an increase in the budget for the Ministry of National Defense, with 157 billion dirhams allocated for the acquisition and maintenance of Royal Armed Forces equipment, as well as support for developing the defense industry.
This increase represents a net rise of approximately 23.7 billion dirhams compared to the previous year, highlighting Morocco’s ongoing trend toward increased defense spending. The aim is to ensure continued funding for major military projects and expand the local defense industry.
According to Article 34 of the draft law, expenditures for acquiring and maintaining military equipment and supporting the national defense industry have been specified under a new defense policy that emphasizes comprehensive modernization and strengthening Morocco’s industrial and security sovereignty.
### Rising Defense Expenditure
The “Military Balance 2025” report published by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) indicates that the Ministry of National Defense’s spending has reached around 4.2% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), reflecting the kingdom’s commitment to enhancing its military capabilities amid a volatile regional environment.
Figures show a consistent increase in the defense budget over recent years: from 96.7 billion dirhams in 2019 to 115.5 billion in 2022, 120 billion in 2023, 124.7 billion in 2024, 133 billion in 2025, and culminating in 157 billion dirhams in 2026. This represents an increase of over 60 billion dirhams within seven years.
### Moroccan Industry
According to “Arab Weekly,” the kingdom aims to modernize its land, air, and naval military capabilities while also developing a national defense industry officially launched in 2020 to reduce dependency on foreign sources.
Morocco is working to strengthen defense partnerships with major powers such as the United States, France, India, China, and Spain. Concurrently, a new legal and regulatory framework aims to attract investments in local military manufacturing, particularly in the aviation and maritime industries, as well as munitions and logistical equipment.
This trajectory reflects a comprehensive strategic vision for localizing defense technology and building an advanced national industrial system, according to royal directives that call for local production of weapons and defense equipment and encourage partnerships with leading Western companies in defense and aerospace technology.
Source